Introduction to the Kingdom of Kush
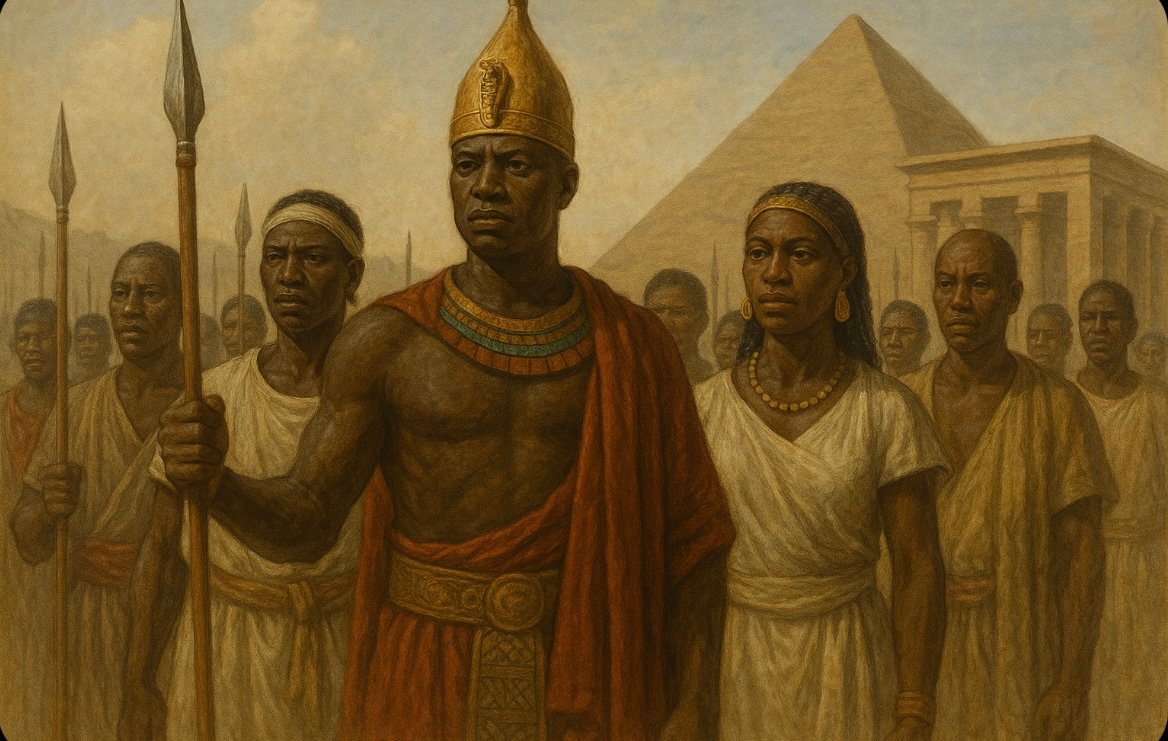
The Kingdom of Kush, an ancient African civilization, thrived in the region known as Nubia, located to the south of ancient Egypt. This kingdom emerged around 1070 BCE, following the decline of the New Kingdom of Egypt, and lasted until approximately 350 CE. The rich history of Kush is marked by its political, cultural, and military significance, making it a formidable rival to the contemporaneous powers, notably ancient Rome.
Kush’s geographical positioning played a crucial role in its development. The kingdom was strategically situated along the Nile River, benefitting from fertile land that facilitated agriculture, trade, and economic prosperity. Its capital cities, notably Kerma, Napata, and Meroë, served as centers of governance and culture, contributing to the civilization’s robust identity. The Kingdom of Kush’s culture was heavily influenced by its proximity to Egypt, resulting in shared religious practices, architectural styles, and burial traditions, while also maintaining unique characteristics distinct to Kushite identity.
Throughout its history, the Kingdom of Kush experienced periods of both peace and conflict, not only with neighboring Egypt but also with emerging powers from the Mediterranean, including the Roman Empire. The Kushites engaged in trade, exchanging goods such as gold, incense, and exotic animals, which enriched their economy and strengthened their international influence. Additionally, they made notable architectural contributions, including the construction of pyramids that rivalled those of Egypt, a testament to their accomplishments in engineering and artistry.
The significance of the Kingdom of Kush lies not only in its political and military achievements but also in its enduring cultural legacy. As a remarkable civilization that flourished in ancient Africa, the Kingdom of Kush paved the way for subsequent societies and continues to be a subject of scholarly interest in understanding the complexity of pre-colonial African history.
Political Structure and Achievements of the Kushite Kingdom
The Kingdom of Kush, located to the south of ancient Egypt, was a remarkable civilization that demonstrated a sophisticated political structure and noteworthy accomplishments. Governed by a series of powerful kings, the Kushite society was organized into a hierarchy that allowed for effective administration and expansion of influence. The kings were often viewed as divine figures, embodying religious and political authority, which legitimized their rule in the eyes of the populace. This unique blend of governance facilitated the unification of the kingdom’s diverse regions, enabling more cohesive decision-making and the centralization of power.
One of the most significant achievements of the Kushite Kingdom was its architectural prowess. The Kushites are perhaps best known for their impressive pyramids, which served as tombs for their pharaohs, similar to those in Egypt but distinct in style and design. These structures not only showcased the advanced engineering skills of the Kushites but also their reverence for the afterlife and their integration of religious beliefs into daily life. Furthermore, monumental temples built in honor of various deities reflected the cultural and religious depth of the society, reinforcing the kings’ divine status while underscoring the significance of spirituality in governance.
In addition to their architectural feats, the Kingdom of Kush excelled in trade and military strategies, making it a notable power in the region. The civilization benefited from its advantageous geographic position, which provided access to vital trade routes connecting Africa and the Mediterranean. This position allowed for the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies with neighboring civilizations, including Rome. The Kushite army, known for its effectiveness in warfare, established a reputation that garnered respect from adversaries and allies alike, further solidifying Kush’s status as a formidable kingdom capable of influencing the broader landscape of ancient power dynamics.
Cultural Exchange and Rivalry with Ancient Rome
The cultural exchange between the Kingdom of Kush and ancient Rome was multifaceted, profoundly influenced by extensive trade routes that interconnected the two civilizations. Located to the south of Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush was strategically positioned to act as a conduit for the exchange of goods and ideas between the African continent and the Mediterranean world. Significant trade interactions fostered the movement of various commodities such as gold, ivory, and exotic animals from Kush, while Rome exported products like wine, glassware, and olive oil, enhancing the material culture of both societies.
One notable aspect of this interaction was the transfer of artistic influences. The Kushites adopted several elements of Roman architectural styles, which can be seen in some of their monumental structures. Conversely, Roman artworks and sculptures increasingly reflected influences from Kushite aesthetics, demonstrating a two-way cultural exchange. This adaptation was not limited to material goods, but extended to ideas as well, including religious practices and philosophies, fostering a greater cultural syncretism.
However, this relationship was not solely characterized by cooperation; it was equally marked by rivalry. The Kingdom of Kush asserted its power through military confrontations with Rome, notably during the reign of the Kushite pharaohs who sought to expand their influence into Egypt. The Roman Empire, recognizing Kush as a formidable rival, employed military strategies and diplomatic maneuvering in attempts to maintain dominance in the region. Key conflicts such as the battles fought over control of trade routes along the Nile highlighted the competitive aspects of this relationship, as both civilizations aimed to secure their place in the ancient world.
As these two powerful kingdoms interacted, their cultural exchanges and rivalry significantly shaped their respective trajectories, contributing to the rich historical tapestry of the ancient Mediterranean and African landscapes.
Legacy of the Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush, which thrived from approximately 1070 BCE to 350 CE, played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural and political landscape of ancient Africa and beyond. Its influence can be traced in various forms, including architecture, trade practices, and governance, and it is noteworthy for the historical interactions it had with neighboring regions, including Egypt. The Kushites developed a complex society characterized by advanced metallurgy, monumental construction, and a rich tapestry of religious beliefs, all of which have left an indelible mark on the area.
The contributions of the Kingdom of Kush are evident in the later civilizations that emerged in the region. For instance, the Nilotic culture, which includes modern-day Sudan and Egypt, was significantly influenced by Kushite traditions in art and governance. The use of pyramids as royal tombs, a hallmark of Kushite architecture, found its way into later South Sudanese and Nubian cultures, illustrating the continuity and adaptation of Kushite legacy. Moreover, the significant documentation of Kushite history, particularly during its reign over Egypt as the 25th Dynasty, highlights its role in reshaping power dynamics in northeastern Africa.
Today, the legacy of the Kingdom of Kush continues to resonate in discussions surrounding African identity and heritage. Preservation of Kush’s history, including critical sites like Meroë, where numerous pyramids and artifacts remain, stands as a testament to its significance in the broader narrative of world history. These sites not only provide insight into Kushite civilization but also serve as a reminder of Africa’s integral role in ancient global interactions. Therefore, understanding and recognizing the contributions of the Kingdom of Kush is essential for a complete interpretation of Africa’s past and its enduring influence on modern society.