Retirement Is a Scam: The System That Keeps You Working Until You Die

They sold us a picture—sunsets, cruises, rocking chairs, and finally “rest.” A promise that if you obeyed long enough, stayed loyal long enough, and worked hard enough, freedom would eventually arrive. But here’s the truth they never put in the brochure: retirement was never designed to free you. It was designed to manage you. From the moment you enter the workforce, the clock starts. Not the one on the wall—but the invisible one counting how long your labor can be extracted before your body slows down. You’re taught to trade the strongest years of your life for a future version of yourself that may never arrive. And if it does arrive, it often shows up tired, sick, underfunded, and still dependent. The system doesn’t ask whether you’ll live long enough to enjoy retirement. It only asks whether you’ll keep contributing. Pensions disappeared quietly. Social Security became “uncertain.” 401(k)s were sold as empowerment while shifting all the risk onto you. Markets go up, markets crash, inflation eats quietly, and fees drain consistently. Meanwhile, you’re told to “stay the course,” even as the goalposts move further away. Retire at 65. No, 67. Maybe 70. Work a little longer. Just a few more years. But here’s the part that exposes the scam completely: the wealthy don’t retire. They don’t stop owning. They don’t stop earning. They don’t wait for permission to rest. They build systems—assets that produce whether they wake up early or sleep in, whether the market is red or green, whether they’re present or absent. While workers are taught to save until the end, owners are taught to cash flow from the beginning. Retirement is a concept designed for people who don’t own anything. If your income stops when you stop working, you are not free—you are leased. And the retirement system simply extends that lease until your final years, hoping your savings outlast your breath. That’s not a plan. That’s a gamble. Inflation makes this even crueler. Every year, the dollar quietly loses strength. What you saved yesterday buys less tomorrow. So even if you “did everything right,” the finish line keeps drifting. Healthcare costs rise faster than savings. Housing becomes unstable. Food gets expensive. Energy costs surge. And suddenly the dream years become survival years. This is why so many retirees go back to work—not because they’re bored, but because the math no longer works. The truth is uncomfortable, but it’s liberating once you see it: the real goal was never retirement. The real goal was dependency. A population waiting on checks, fearful of market swings, hesitant to speak up, cautious not to disrupt the system they rely on. Ownership breaks that spell. When you own cash-flowing assets—businesses, real estate, royalties, equity—you don’t wait for retirement. You design your life in phases. You shift labor into leverage. You trade time-for-money income for money-that-produces-more-money. That’s the path they don’t emphasize, because it doesn’t keep you predictable. This doesn’t mean rest is wrong. It means postponing life until the end is a trap. Freedom isn’t an age. It’s a structure. And the earlier you build that structure, the less power the system has over you. You don’t need millions to start. You need clarity. You need a shift from “How do I save enough?” to “How do I own enough?” You need income streams that don’t expire at 65. You need education that focuses on assets, not just employment. Retirement is a scam—but exiting the scam is possible. The moment you stop chasing a finish line and start building a foundation, everything changes. You stop asking for permission. You stop waiting. You stop hoping the system keeps its promise. Because it never planned to. And that’s the quiet truth they never taught us—but the one that changes everything once you understand it. ❤️ Support Independent Black Media Black Dollar & Culture is 100% reader-powered — no corporate sponsors, just truth, history, and the pursuit of generational wealth. Every article you read helps keep these stories alive — stories they tried to erase and lessons they never wanted us to learn. This is why conversations like this matter. Not to scare you—but to wake you up. If this perspective shifted something in you, share it, bookmark it, and start asking different questions about money, ownership, and freedom. The exit from the trap doesn’t begin at retirement—it begins with what you build right now.👉 Read more and build with us at BlackDollarCulture.blog Hashtags#RetirementIsAScam #BlackDollarCulture #WealthEducation #FinancialFreedom #OwnershipMindset #GenerationalWealth #AssetsOverIncome #EscapeTheSystem #BuildTheBlock Focus Keyphrase: Retirement is a scamMeta Description: Retirement is a scam designed to keep workers dependent while owners build freedom. Learn why ownership—not retirement—is the real path to financial independence.Slug: retirement-is-a-scam
Money Rules the Rich Teach Their Kids (But Never Say Out Loud)

In certain households, money is never treated as a mystery. It’s not emotional, not dramatic, and not taboo. It’s discussed quietly, observed daily, and understood long before adulthood. Wealthy families rarely sit their children down and announce that they are about to teach them “the secrets of money.” Instead, they teach through behavior, structure, and repetition. By the time their children grow up, they don’t just earn money — they control it. One of the first unspoken lessons is that money is not the goal. In wealthy homes, money is framed as a tool. It exists to buy time, flexibility, and options. Children raised in these environments don’t chase money for validation. They learn that money is useful, but never emotional. This alone changes decision-making for life. When money loses its emotional charge, logic replaces impulse. Another quiet rule is that assets come before lifestyle. Wealthy parents do not rush to upgrade their lives every time income increases. Children grow up watching adults acquire businesses, equity, or income-producing assets before buying luxuries. The message isn’t spoken — it’s demonstrated. Lifestyle is something assets pay for, not something income is sacrificed to maintain. This creates patience and discipline that most people never develop. Jobs are also framed differently. In many households, a job is treated as the ultimate achievement. In wealthy families, a job is simply seed capital. Children hear conversations about using income to fund investments or ownership. Work is never positioned as identity. It’s positioned as leverage. As a result, wealthy children don’t grow up asking how to climb the ladder — they ask how to exit it. Ownership is the core principle behind everything. Cash is seen as temporary, while assets are permanent. Wealthy children grow up around deeds, shares, businesses, and partnerships. They understand early that ownership creates control, stability, and power. Saving money is respected, but hoarding cash is not glorified. Cash that isn’t deployed is seen as idle potential. Debt is another concept that’s handled with precision. In many families, debt is feared or misunderstood. In wealthy households, debt is treated like a tool that can either build or destroy depending on how it’s used. Children see debt used to acquire income-producing assets, never depreciating purchases meant for status. This distinction becomes second nature. Taxes are never framed emotionally either. Wealthy families don’t complain about taxes — they plan around them. Children overhear conversations about structure, strategy, and legal optimization. They learn early that taxes are not a punishment for success, but a penalty for ignorance. This understanding alone saves wealthy families millions over generations. One of the most powerful lessons is rarely spoken aloud: never sell an appreciating asset if you can borrow against it. Wealthy families hold onto assets and use loans for liquidity. This keeps ownership intact while allowing access to cash. Children raised with this mindset understand that selling stops compounding, while borrowing preserves it. Time is emphasized more than timing. Wealthy families teach patience by example. Children watch compounding happen slowly, then suddenly. They learn that starting early matters more than being perfect. Fast money loses its appeal when long-term growth proves unstoppable. Risk is not avoided — it’s managed. Wealthy parents don’t raise fearful children. They raise informed ones. Through diversification, insurance, and long-term planning, risk is reduced to something measurable rather than something terrifying. Children learn that avoiding risk entirely guarantees stagnation. Lifestyle inflation is quietly resisted. As income rises, expenses remain controlled. Children see adults live below their means while assets expand behind the scenes. This discipline protects future freedom and prevents wealth from leaking away unnoticed. Network is treated as an asset as well. Wealthy children grow up in environments where opportunity feels normal. Rooms matter. Conversations matter. Access changes outcomes faster than effort alone. This exposure shapes expectations for life. Perhaps the most important lesson is that wealth is taught at home. Schools are never relied upon to teach money. Children learn through participation, observation, and real-world involvement. Family discussions replace financial secrecy. Transparency replaces confusion. Finally, wealthy families value privacy. Quiet wealth is protected wealth. Flash is avoided. Attention is unnecessary. Power moves silently. Children learn that true wealth doesn’t need applause. By the time wealthy children become adults, the rules are already embedded. They don’t chase money. They deploy it. They don’t fear it. They control it. And that is the difference no one ever says out loud. Focus Keyphrase: money rules the rich teach their kids Meta Description: Explore the unspoken money rules wealthy families teach their children—covering assets, ownership, debt, taxes, discipline, and legacy thinking schools never explain. Slug: money-rules-the-rich-teach-their-kids
If Your Phone Is Making Money While You Sleep, You’ve Escaped the System

Most people go to sleep hoping tomorrow will be better. Sir Wealthington goes to sleep knowing tomorrow already paid him. That difference is everything. While the world teaches us to grind harder, wake up earlier, and trade more hours for dollars, the wealthy quietly build systems that work whether they’re awake or not. That’s why the image of Sir Wealthington sleeping peacefully while his phone lights up with money notifications isn’t fantasy — it’s a blueprint. Because real wealth doesn’t clock in. It compounds. For decades, Black communities have been taught survival instead of ownership. We were trained to hustle for checks instead of designing systems that generate them. The result? Exhaustion, burnout, and generations stuck restarting instead of scaling. Money that only pays you when you’re awake isn’t freedom. It’s dependency. The truth is simple but uncomfortable: if your income stops when you stop working, you don’t own your time — your job does. And no matter how good the salary looks on paper, time is the only asset you can’t refinance, renegotiate, or replace. This is where passive income gets misunderstood. It’s not about doing nothing. It’s about doing the right work once — then letting it pay you repeatedly. Sir Wealthington didn’t fall asleep rich. He engineered it. He built assets that notify him instead of supervisors. His phone doesn’t buzz with alarms — it buzzes with confirmations. Dividends clearing. Digital sales closing. Royalties posting. Interest compounding. Systems executing. That’s the goal. The wealthy don’t ask, “How much can I make this month?”They ask, “What can I build that pays me forever?” This mindset shift is critical. Because earned income has limits. There are only so many hours in a day. But ownership income has no ceiling. One asset can pay you a hundred times, a thousand times, or a million times over without asking for overtime. Think about it: music artists sleep while streams generate revenue. Authors sleep while books sell. Investors sleep while dividends hit accounts. Business owners sleep while systems operate. Workers sleep hoping their alarm doesn’t go off too early. That’s not accidental. That’s design. And design starts with understanding the difference between income and wealth. Income feeds you today. Wealth feeds generations. This is why wealthy families prioritize assets early. They buy cash-flowing tools before luxury toys. They reinvest before they reward themselves. They make money boring before they make it flashy. Sir Wealthington’s pajamas tell the story. Covered in dollar signs, but calm. No stress. No scramble. No panic. Because systems don’t panic — people do. Ownership brings peace. Systems bring sleep. Now let’s be clear: passive income is not lazy income. It requires discipline, patience, and delayed gratification. But unlike a job, the work is front-loaded. You build once, refine often, and collect continuously. That’s why many never reach it — they want immediate comfort instead of long-term leverage. Black wealth doesn’t disappear because we don’t work hard. It disappears because we were never taught to lock it in. To structure it. To protect it. To make it repeat. The system didn’t reward ownership education. It rewarded compliance. But the moment you understand how money works while you sleep, everything changes. You stop asking for raises and start building revenue streams. You stop chasing promotions and start acquiring positions. You stop worrying about layoffs because your income isn’t tied to someone else’s decisions. This is the real flex: peace. Imagine sleeping without anxiety because your bills are automated and your income is diversified. Imagine waking up without urgency because your assets already moved while you rested. That’s not luck. That’s leverage. Sir Wealthington doesn’t check his phone in the morning with fear. He checks it with confirmation. And this isn’t reserved for the elite. Digital assets, dividend investing, intellectual property, automated businesses, licensing, and ownership structures are more accessible today than ever before. The barrier isn’t access — it’s mindset. If you’re still trading hours for survival, you’re playing defense. Wealth requires offense. The goal isn’t to work less — it’s to work smarter, then let the work outlive the effort. Money that sleeps with you is loyal. Money that only pays when you show up is temporary. The real question isn’t whether you can build income streams.It’s whether you’re willing to stop being comfortable long enough to design them. Sir Wealthington didn’t escape the system by accident.He replaced it. And tonight, while most people sleep hoping,his phone will buzz again. ❤️ Support Independent Black Media Black Dollar & Culture is 100% reader-powered — no corporate sponsors, just truth, history, and the pursuit of generational wealth. Every article you read helps keep these stories alive — stories they tried to erase and lessons they never wanted us to learn. Focus Keyphrase: money working while you sleepSlug: money-working-while-you-sleepMeta Description: Discover why real wealth is built through systems that generate income while you sleep — and how ownership, not hustle, creates peace and generational power.
How to Build a Business That Runs Without You

The Blueprint for True Freedom, Ownership, and Scale Most people say they want to own a business, but what they really end up building is a job with a logo. If the business collapses the moment you stop answering emails, posting content, or showing up every day, you don’t own a business—you own a dependency. True wealth comes from building systems that work whether you’re present or not. This is how the wealthy buy back their time, protect their energy, and scale beyond effort. Building a business that runs without you isn’t about laziness. It’s about design. It’s about removing yourself as the bottleneck and replacing hustle with structure, clarity, and automation. This guide breaks down exactly how to do that. 1. Start With the End in Mind (Owner vs Operator Thinking) The first shift is mental. You must decide early whether you’re building: An operator asks: What do I need to do today?An owner asks: What system needs to exist so this doesn’t require me? Every task you do manually today should be viewed as temporary. If you don’t design your business with replacement in mind, you’ll trap yourself inside it. Ask yourself: Those answers reveal exactly what must be systemized. 2. Choose a Business Model That Can Actually Scale Not every business is meant to run without you. Some models are naturally scalable, others fight you at every step. High-leverage models include: Low-leverage models include: If your income depends on your physical presence or constant customization, freedom will always be limited. The goal is repeatability, not perfection. 3. Document Everything You Do (Before You Delegate Anything) Most people try to hire help too early and fail because they never defined the work. Before you outsource or automate, you must document your processes: This can be as simple as: If someone can’t follow instructions to replace you, the system—not the worker—is the problem. 4. Turn Repetition Into Automation Anything repetitive should be automated before it’s delegated. Examples: Automation removes human error and emotional burnout. It also makes your business more valuable because systems don’t quit. Key areas to automate first: 5. Build a Team Around Roles, Not People A business that runs without you is built on roles, not personalities. Instead of saying: Say: This allows you to: Start with part-time or contract help: Your job is not to do the work—it’s to manage the system that produces the work. 6. Separate Ownership From Operations One of the most powerful moves you can make is separating: As the owner, your responsibilities should eventually shrink to: If you’re still stuck in daily execution years in, the business owns you. True freedom happens when: 7. Build Systems That Make Decisions Without You The highest level of leverage is decision automation. This includes: When your business has rules, it doesn’t need constant supervision. When everything requires your opinion, burnout is inevitable. Document your values and standards so your team and systems know how to act even when you’re absent. 8. Create Predictable Cash Flow First A business that runs without you must be financially stable. Focus on: Chaos in cash flow forces you back into survival mode, which kills system-thinking. Stability buys you space. Space allows structure. 9. Design the Exit Even If You Never Leave Every strong business is built as if it will be sold—even if you never sell it. That means: A business that can be sold is a business that can run without you. Even if you never exit, you gain leverage, freedom, and peace. 10. Measure Freedom, Not Just Revenue Revenue without freedom is a trap. Track: The real flex isn’t working nonstop—it’s earning while absent. Final Thought A business that runs without you is not built overnight. It’s built deliberately. Every system you create is a brick in the wall separating your income from your time. That separation is the foundation of generational wealth. Most people chase money. Owners design freedom. Build accordingly. Focus Keyphrase: build a business that runs without youMeta Description: Learn how to build a business that runs without you using systems, automation, and scalable models. A step-by-step blueprint for true freedom and ownership.Slug: build-a-business-that-runs-without-you
Frederick McKinley Jones: The Black Inventor Who Revolutionized Refrigeration and Global Food Supply

Before refrigerated trucks, the world ate locally, lived seasonally, and lost enormous amounts of food to spoilage. Fresh meat rarely traveled far. Produce rotted before reaching cities. Vaccines and blood plasma often expired before arriving where they were needed most. Entire regions were constrained not by demand, but by distance. Modern life as we know it simply wasn’t possible yet. That reality changed because of Frederick McKinley Jones. Born in 1893, Jones did not grow up with access to elite schools, laboratories, or wealthy patrons. He was largely self-taught, learning mechanics, engineering, and electronics through curiosity and necessity rather than formal education. In an America that routinely dismissed Black intelligence, Jones quietly mastered complex systems that others struggled to understand. He fixed machines. He improved them. And eventually, he redesigned an entire industry from the ground up. Jones recognized a problem most people had accepted as unavoidable: perishable goods could not survive long journeys. The solution wasn’t simply ice or insulation. It required a compact, reliable, mobile system capable of maintaining controlled temperatures while in motion. At the time, that idea bordered on impossible. Vehicles vibrated. Engines overheated. Roads were rough. Power sources were inconsistent. Yet Jones engineered a self-contained refrigeration unit strong enough to withstand travel and precise enough to preserve food and medicine. His invention of mobile refrigeration systems transformed transportation forever. Trucks, trains, and ships could now carry fresh goods across long distances without loss. Farms were no longer limited to nearby markets. Cities could grow larger without risking food shortages. Seasonal eating gave way to year-round availability. Grocery stores evolved. Supply chains expanded. Entire industries were born almost overnight. The impact reached far beyond food. During World War II, Jones’s refrigeration technology was used to transport blood plasma and medical supplies to soldiers overseas. Lives were saved not by battlefield heroics, but by temperature control. Quiet engineering became silent survival. Jones went on to earn more than sixty patents across refrigeration, engines, and electronics. He co-founded what would later become Thermo King, a company that still dominates global refrigeration transport today. Billions of dollars move through systems built on his ideas. Every refrigerated truck on the highway traces its lineage back to his work. And yet, for decades, his name was absent from classrooms, textbooks, and mainstream discussions of American innovation. This pattern is not accidental. Black inventors have repeatedly solved foundational problems only to watch their contributions be absorbed, rebranded, and monetized by others. The wealth generated often never returned to the communities that produced the ideas. Recognition arrived late, if at all. Frederick McKinley Jones was eventually awarded the National Medal of Technology, becoming the first Black American to receive the honor. It was deserved, but overdue. By then, the world had already been built on his inventions. At Black Dollar & Culture, these stories matter because they reveal something deeper than history. They show how wealth is created at the systems level. Jones didn’t invent a product. He invented infrastructure. He didn’t chase trends. He solved a permanent problem. That is where real leverage lives. Understanding his legacy is not about admiration alone. It is about strategy. Ownership. Protection. Continuity. When we study figures like Jones, we see a blueprint for how generational wealth is actually built — not through visibility, but through necessity and control of essential systems. Every cold chain, every vaccine shipment, every refrigerated aisle is proof that Black innovation has always powered the modern world, even when the world refused to acknowledge it. The work was never invisible. Only the credit was. ❤️ Support Independent Black Media Black Dollar & Culture is 100% reader-powered — no corporate sponsors, just truth, history, and the pursuit of generational wealth. Every article you read helps keep these stories alive — stories they tried to erase and lessons they never wanted us to learn. Slug: frederick-mckinley-jones-black-inventor-refrigerationMeta Description: Frederick McKinley Jones was a Black inventor whose mobile refrigeration technology transformed food distribution, medicine, and global trade.entor whose mobile refrigeration technology transformed food, medicine, and global trade. Learn the story they don’t teach.Slug: frederick-mckinley-jones-black-inventor-refrigeration
Black-Owned Businesses: Why Pouring Back Into the Community Is the Ultimate Power Move

This isn’t about charity. It’s about strategy.When Black-owned businesses reinvest into the communities that support them, they aren’t giving money away — they’re locking in longevity, loyalty, and leverage. History proves it. Modern data confirms it. And the future demands it. Before desegregation, before outside corporations flooded our neighborhoods, Black communities circulated the dollar dozens of times before it ever left. That circulation built schools, banks, hospitals, newspapers, and generational wealth. The collapse didn’t happen because the model failed — it happened because the system was disrupted. Here’s why pouring back in is not optional, but essential. 1. Community Investment Multiplies Business Survival Money spent locally doesn’t disappear — it cycles.When a Black business hires locally, sources locally, or sponsors locally, the community becomes economically invested in that business’s survival. That’s how you create customers who don’t just buy once — they defend your brand. • Local Jobs create Stable customers• Local Vendors reduce Costs and dependencies• Local Loyalty increases Lifetime value A supported community protects its own. 2. Wealth Circulation Builds Economic Immunity Every dollar that leaves the community weakens it.Every dollar that stays strengthens it. When Black businesses reinvest — through scholarships, youth programs, apprenticeships, or community real estate — they reduce dependency on outside systems that were never designed to protect us. This isn’t emotional. It’s mathematical. 3. Reinvestment Creates the Next Generation of Owners Communities don’t rise by consumption alone — they rise by ownership transfer. When successful Black businesses mentor youth, fund internships, or teach financial literacy, they aren’t just helping — they’re creating future partners, suppliers, and successors. Ownership is taught. Power is modeled. 4. Trust Is the New Currency In a world of ads, algorithms, and distractions, trust beats marketing. A business that visibly pours back into the community earns:• Word-of-mouth growth• Free brand ambassadors• Crisis-proof support People support what supports them. 5. Economic Power Is Political Power (Without Politics) You don’t need permission when you control resources. Communities with strong local businesses:• Fund their own initiatives• Solve problems internally• Negotiate from strength Reinvestment turns neighborhoods into economic blocs, not begging grounds. 6. The Blueprint Already Exists We don’t need new ideas — we need discipline and execution. From Greenwood (Black Wall Street) to Durham’s Black banking class, history shows that community-centered business models work when we commit to them long-term. The goal isn’t to escape the community — it’s to elevate it with you. The Bottom Line Black-owned businesses that pour back into the community don’t shrink — they compound. This is how legacies are built.This is how ecosystems form.This is how wealth stops leaking and starts circulating. 👉 Read more stories like this — and learn how ownership really works. ❤️ Support Independent Black Media Black Dollar & Culture is 100% reader-powered — no corporate sponsors, just truth, history, and the pursuit of generational wealth. Every article you read helps keep these stories alive — stories they tried to erase and lessons they never wanted us to learn. #BlackOwnedBusiness #BlackWealth #EconomicPower #CommunityEconomics #BuyBlack #GenerationalWealth #BlackDollar #OwnershipMindset #BlackEntrepreneurs Focus Keyphrase: Black owned businesses community reinvestmentSlug: black-owned-businesses-community-reinvestmentMeta Description: Why Black-owned businesses pouring back into the community isn’t charity — it’s a proven strategy for wealth circulation, loyalty, and generational power.
Why Gold Protects Wealth When Markets Collapse

Markets don’t collapse overnight—they unravel quietly, then all at once. Long before the headlines turn red and panic becomes fashionable, confidence begins to erode beneath the surface. Liquidity tightens, assumptions fail, and investors realize—too late—that optimism was doing more work than fundamentals. When that confidence breaks, gold does what it has always done: it holds. Gold has never been an asset of excitement. It doesn’t trend on social media, it doesn’t promise outsized returns, and it doesn’t rely on narratives. It exists for moments of stress—when systems are questioned, currencies are diluted, and trust in leadership weakens. After surviving multiple market cycles, one lesson becomes unavoidable: markets reward growth, but wealth survives through protection. When stock markets collapse, it’s rarely because companies disappear overnight. It’s because valuations were built on fragile assumptions—cheap money, endless growth, stable geopolitics. Once those assumptions crack, repricing is swift and unforgiving. Gold doesn’t reprice on earnings calls or guidance forecasts. It responds to fear, uncertainty, and instability—the very conditions that define market collapses. Cash feels safe during chaos, but history exposes its weakness. Inflation quietly erodes purchasing power while governments respond to crises with stimulus, debt expansion, and money creation. Every collapse is met with liquidity, and liquidity always comes at a cost. Gold has no printing press. Its scarcity is real, which is why it preserves value when paper assets struggle to do the same. This is precisely why central banks hold gold. Not for tradition—but for credibility. When trust between nations weakens, gold becomes neutral ground. When debt loads grow uncomfortable, gold becomes reassurance. When currencies wobble, gold becomes stability. The same logic applies at the individual level. Another overlooked advantage of gold during market collapses is optionality. The most dangerous position an investor can be in during a downturn is forced selling. Gold provides liquidity without forcing the liquidation of productive assets at the worst possible moment. It buys time, and time is often the difference between recovery and permanent loss. Gold also behaves differently than most assets during crises. While correlations across markets tend to spike during panic, gold often diverges. It may not surge immediately, but it holds ground while others fall. That stability matters far more than aggressive upside when the goal is wealth preservation. The wealthy understand this distinction clearly. They don’t buy gold to outperform equities in bull markets. They hold it to survive bear markets. Gold is not designed to make headlines—it’s designed to protect capital when headlines turn ugly. History reinforces this lesson repeatedly. Empires rise and fall. Currencies are introduced, abused, and replaced. Financial systems evolve, break, and rebuild. Through every version of that cycle, gold remains relevant—not because it is old, but because it is independent. Gold does not replace businesses, real estate, or equities. It complements them. Think of it as structural support rather than decoration. You don’t admire it when times are calm, but without it, the foundation cracks under pressure. When markets collapse, emotions spread faster than facts. Gold does not react to emotion. It doesn’t panic, doesn’t promise, and doesn’t explain itself. It simply holds value while everything else explains why it can’t. That is why gold protects wealth—not through excitement, but through endurance. ❤️ Support Independent Black Media Black Dollar & Culture is 100% reader-powered — no corporate sponsors, just truth, history, and the pursuit of generational wealth. Every article you read helps keep these stories alive — stories they tried to erase and lessons they never wanted us to learn. Focus Keyphrase:gold protects wealth Slug:why-gold-protects-wealth-when-markets-collapse Meta Description:When markets collapse and confidence disappears, gold has historically protected wealth. Learn why gold remains a powerful hedge during economic uncertainty.
Tuskegee Airmen Black History: The Elite Pilots Who Forced America to End Military Segregation

January 12, 1942 did not arrive with parades, speeches, or national celebration, but history often moves quietly before it roars. On this winter day, in a nation still shackled by segregation and racial mythology, the United States Army Air Forces authorized a program that would challenge one of America’s most deeply held lies: the belief that Black men lacked the intelligence, discipline, and courage to fly military aircraft. From this authorization emerged the men later known as the Tuskegee Airmen—a group whose excellence in the skies would force the nation to confront its contradictions. ❤️ Support Independent Black Media Black Dollar & Culture is 100% reader-powered — no corporate sponsors, just truth, history, and the pursuit of generational wealth. Every article you read helps keep these stories alive — stories they tried to erase and lessons they never wanted us to learn. The establishment of the Tuskegee program did not come from sudden enlightenment. It was the result of pressure, protest, and necessity. Black leaders, civil rights organizations, and newspapers had long challenged the military’s refusal to allow Black pilots, pointing out the hypocrisy of fighting for democracy abroad while denying it at home. World War II, with its demand for manpower, created a crack in the wall. The government conceded, but only partially, and under tightly controlled conditions designed less to empower Black airmen than to test them under a microscope. Training took place at Tuskegee Army Air Field in Alabama, a segregated base in a segregated state. The pilots were trained separately from white counterparts, often with inferior resources, outdated equipment, and instructors who expected failure. Every mistake by a Black cadet was magnified, recorded, and used as supposed proof of racial inferiority. No white unit trained under such pressure. These men were not simply learning to fly; they were fighting an unspoken trial in which the future of Black military aviation hung on every maneuver. Despite these conditions, the men excelled. They mastered navigation, aerial combat, engineering, and leadership. Many already held college degrees at a time when higher education was still largely denied to Black Americans. Their discipline was not accidental—it was forged from the understanding that mediocrity would not be tolerated. Excellence was the minimum requirement for survival, dignity, and progress. When the Tuskegee Airmen were finally deployed overseas, they were assigned to escort Allied bombers deep into enemy territory. This was among the most dangerous missions of the war. Bomber crews depended on fighter escorts to protect them from German aircraft; failure meant death. The Tuskegee Airmen, later known as the “Red Tails” for the distinctive markings on their planes, built a reputation for precision and loyalty. They stayed with the bombers. They did not abandon their posts for personal glory. As a result, they achieved one of the lowest bomber-loss rates of any fighter group in the war. This success directly contradicted decades of pseudoscience and propaganda used to justify segregation. The myth that Black men lacked the mental acuity for complex machinery collapsed under the weight of facts written in combat reports and survival statistics. The myth that Black men lacked courage evaporated in the skies over Europe. What remained was an uncomfortable truth: the barrier had never been ability—it had been racism. Yet recognition did not come easily. While white pilots were celebrated in newsreels and headlines, the Tuskegee Airmen returned home to a country still governed by Jim Crow. They could defeat fascism abroad but not segregation at home. Many were denied jobs in commercial aviation. Some were refused service in restaurants while still wearing their uniforms. The nation had used their skill but hesitated to honor their humanity. Still, history has a long memory, even when institutions try to forget. The success of the Tuskegee Airmen became impossible to ignore. Their record played a crucial role in the 1948 decision by President Harry S. Truman to desegregate the U.S. military, a move that reshaped American armed forces and set a precedent for broader civil rights reforms. Though Truman signed the order, it was the Airmen who earned it with their lives and discipline. The legacy of the Tuskegee Airmen is not confined to military history. It is a lesson in how systems preserve themselves through lies, and how those lies collapse when confronted by undeniable excellence. It is also a reminder that progress in America has rarely been gifted; it has been extracted through pressure, performance, and sacrifice. These men did not simply ask to be included—they proved that exclusion was irrational. Today, when their story is told accurately, it reframes how we understand Black history. It challenges narratives that portray Black advancement as sudden or accidental. The Tuskegee Airmen were scholars, engineers, tacticians, and leaders operating under extreme constraints. Their success was not a fluke; it was the continuation of a long tradition of Black mastery systematically obscured from public memory. January 12 should be remembered not merely as a date, but as a turning point where the lie began to crack. On that day, the United States unknowingly authorized the dismantling of one of its own racist doctrines. The men who trained at Tuskegee did more than learn to fly. They redefined what the nation could no longer deny. They turned the sky into a courtroom, and every successful mission became a verdict. Their story is not just about airplanes or war. It is about truth. And once truth takes flight, it is very hard to bring back down. Focus Keyphrase: Tuskegee Airmen Black HistoryMeta Description: Explore the true story of the Tuskegee Airmen, the Black pilots who shattered racist myths during World War II and reshaped American military history.Slug: tuskegee-airmen-black-history
Granville T. Woods: The Black Inventor Who Electrified Modern America
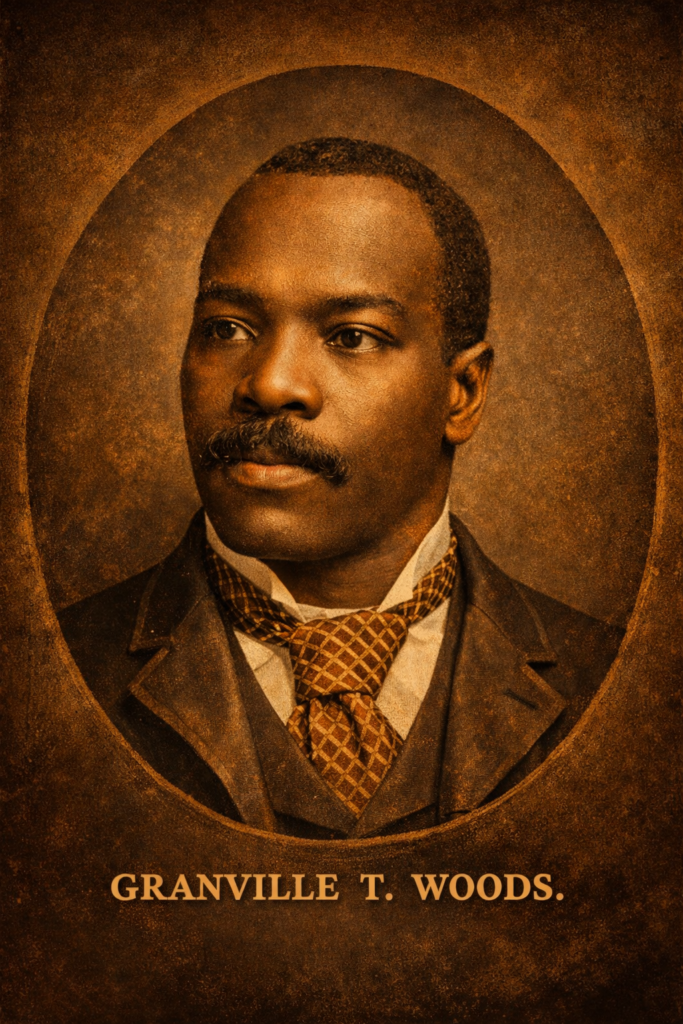
Long before America celebrated innovation as a corporate achievement, before patents became weapons and genius was filtered through race and power, a self-taught Black engineer was quietly reshaping the future of the nation. His name was Granville T. Woods, and the modern world still runs on systems influenced by his mind, even if history has tried to forget him. Born in 1856 in Columbus, Ohio, just one year after the official end of slavery, Woods entered a country that had little interest in protecting Black intellect. Formal education was limited, but necessity became his classroom. As a teenager, he worked in machine shops, steel mills, and on railroads, absorbing mechanical knowledge firsthand. Where others saw labor, Woods saw systems. Where others followed instructions, he asked why things worked—and how they could work better. Railroads in the late 19th century were expanding rapidly, but they were also deadly. Trains collided frequently because communication between moving locomotives and stations was unreliable. Signal systems lagged behind the speed of industrial growth, and passengers paid the price. Woods recognized electricity as the missing link. At a time when electrical engineering was still in its infancy, he envisioned wireless communication between trains and control stations—an idea well ahead of its time. That vision became reality through his invention of the induction telegraph. This system allowed trains to communicate with stations and other trains without physical wires, drastically reducing collisions and improving coordination across rail networks. It was not a minor upgrade; it was a foundational leap in transportation safety. Modern rail signaling, subway communication systems, and even elements of wireless transit technology trace conceptual roots back to Woods’ work. But invention was only half of Woods’ struggle. Ownership was the other. In an America where white inventors were celebrated and Black inventors were questioned, Woods was forced into constant legal battles to defend his patents. Powerful industrial figures challenged his claims, attempting to absorb his ideas into their own portfolios. Among them was Thomas Edison, one of the most famous inventors in American history. Edison disputed several of Woods’ patents, particularly those related to electrical transmission and communication systems. The legal battles were not symbolic—they were brutal, expensive, and exhausting. Yet Woods won. Multiple courts ruled in his favor, affirming that his ideas were original and his claims legitimate. These victories were rare for a Black inventor in that era and underscored the undeniable brilliance of his work. Ironically, after losing to Woods in court, Edison offered him a position at Edison Electric Light Company. Woods declined. He understood that employment would mean surrendering independence and potentially losing control of future inventions. Instead, he chose the harder path: remaining an independent inventor in a system stacked against him. Woods’ contributions extended far beyond railroads. He held more than 60 patents, many focused on electrical systems, power distribution, and transportation. His work improved electric streetcars, helped develop overhead power lines, and advanced the efficiency of electrical transmission in growing cities. Urban America—its subways, trolleys, and commuter systems—benefited enormously from his innovations. Yet unlike his white contemporaries, Woods did not amass wealth. Patent litigation drained his resources. Corporations profited from his ideas while he struggled to maintain financial stability. By the time of his death in 1910, he was respected among engineers but virtually invisible to the public. No fortune. No national recognition. No textbooks honoring his name. This pattern was not accidental. It reflected a broader American reality: Black innovation was essential, but Black ownership was optional. Woods’ story mirrors countless others where genius was extracted, repackaged, and monetized by institutions that refused to credit its true source. His life exposes the uncomfortable truth that America’s technological rise was fueled not just by celebrated inventors, but by marginalized minds denied their rightful place in history. Today, as conversations around equity, ownership, and intellectual property resurface, Granville T. Woods’ story feels painfully modern. He was not merely a victim of his time; he was a warning. Innovation without protection leads to exploitation. Genius without ownership leads to erasure. Restoring Woods to his rightful place is not about nostalgia. It is about understanding the foundation of modern America. The trains that move millions each day, the communication systems that ensure their safety, and the electrical infrastructure that powers cities all carry echoes of his work. His fingerprints are everywhere, even when his name is not. Granville T. Woods was more than an inventor. He was proof that Black intellect has always been central to progress—even when history refused to acknowledge it. Remembering him is not rewriting history. It is finally telling it honestly. Focus Keyphrase: Granville T. Woods Black InventorSlug: granville-t-woods-black-inventorMeta Description: Granville T. Woods was a brilliant Black inventor whose electrical innovations transformed railroads and powered modern America, including winning patent cases against Thomas Edison.
Bessie Coleman: The Woman Who Refused to Stay Grounded

Bessie Coleman was born on January 26, 1892, in Atlanta, Texas, at the intersection of poverty, racism, and rigid limitation. She was the tenth of thirteen children born to George and Susan Coleman, a family of sharecroppers whose lives were shaped by the unforgiving realities of post-Reconstruction America. Cotton fields, long days, and scarce opportunity defined her early years. Education existed, but barely—one-room schoolhouses, worn textbooks, and interrupted learning whenever farm labor demanded it. Yet even in those conditions, Bessie showed an early hunger for knowledge, discipline, and something beyond the horizon. Her father eventually left the family, returning to Indian Territory in Oklahoma in search of a better life, while Bessie remained with her mother, helping raise her siblings and working the fields. Poverty was not an abstract concept to her; it was lived daily. But so was resilience. She excelled in school when she could attend, eventually saving enough money to enroll at Langston University in Oklahoma. Her time there was short—financial hardship forced her to withdraw—but the seed of ambition had already taken root. She would not accept a life dictated by circumstance. In her early twenties, Bessie moved to Chicago, joining the Great Migration of Black Americans seeking opportunity beyond the South. There, she worked as a manicurist, a job that placed her in close proximity to conversation, news, and stories from beyond her world. It was in a barbershop that her life took its decisive turn. She listened as Black men returned from World War I spoke of flying in Europe. They talked about airplanes, freedom, and skies that did not feel segregated. Her brothers, particularly one who had served in France, taunted her—telling her that French women could fly planes while American Black women could not. Instead of discouraging her, the insult ignited something irreversible. Bessie Coleman decided she would fly. The problem was America had no intention of letting her do so. Every aviation school she applied to rejected her. The rejections were absolute—no appeals, no alternatives. She was dismissed not for lack of intelligence or ability, but because she was both Black and a woman. In the early 20th century, flight was considered the domain of white men only. Rather than accept the denial, Bessie made a decision that defined her legacy: if America would not teach her, she would leave America. She enrolled in French language classes, saved her earnings meticulously, and gained sponsorship from influential Black newspapers, including the Chicago Defender. In 1920, she sailed to France. This alone was radical—an unmarried Black woman traveling abroad for professional training at a time when many Americans never left their home counties. In France, she trained at the Caudron Brothers’ School of Aviation, one of the most respected flight schools in the world. Flying in the 1920s was not glamorous. Planes were unstable, cockpits open to the elements, and crashes common. Training involved risk at every step. Bessie endured crashes, injuries, and intense discipline. But she persisted. On June 15, 1921, she earned her international pilot’s license from the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale, becoming the first Black woman in the world to do so—and one of the first Americans of any race to hold that distinction. When Bessie returned to the United States, her achievement should have made her a national hero. Instead, she encountered the same walls she had left behind. Airlines would not hire her. Commercial aviation opportunities were closed. Once again, racism tried to ground her ambitions. This time, she refused to stop moving forward. Bessie turned to barnstorming—performing aerial stunts at airshows across the country. Loop-the-loops, dives, figure-eights—she mastered them all. But her performances were not about spectacle alone. They were statements. Every time she climbed into a cockpit, she challenged the idea that Black people belonged only on the ground. She attracted massive crowds, especially in Black communities, where many had never seen an airplane up close, let alone one piloted by a Black woman. She was also uncompromising in her principles. Bessie refused to perform at venues that enforced segregated seating. If Black spectators were forced to enter through back gates or sit separately, she would not fly. This stance cost her income and opportunities, but she would not trade dignity for exposure. To her, flight symbolized freedom, and freedom could not exist alongside humiliation. Her vision extended far beyond stunt flying. Bessie dreamed of opening a flight school for Black aviators—men and women—so future generations would not have to leave the country to learn what she had fought to access. She spoke publicly about this goal, emphasizing education, discipline, and ownership of the skies. She wanted Black pilots, Black mechanics, Black instructors—an aviation ecosystem independent of exclusionary systems. Tragically, that dream was cut short. On April 30, 1926, in Jacksonville, Florida, Bessie Coleman boarded a plane for a practice flight ahead of an upcoming airshow. The aircraft was piloted by her mechanic, William Wills. Bessie was not wearing a seatbelt because she was scouting the terrain below, preparing for a parachute jump she planned to perform later. Mid-flight, the plane experienced a mechanical failure—later determined to be caused by a loose wrench lodged in the engine. The aircraft went into a sudden nosedive. Bessie was thrown from the plane at 2,000 feet and died instantly. She was 34 years old. Moments later, the plane crashed, killing Wills as well. Her death sent shockwaves through Black communities across the country. Thousands attended her funeral in Chicago. Leaders, activists, and ordinary people mourned not just the loss of a woman, but the loss of a future she represented. She died without ever opening the flight school she envisioned, without seeing the aviation doors she cracked open fully swing wide. Yet her impact did not end with her life. Bessie Coleman became a symbol—of courage without permission, of ambition without apology. Her legacy inspired future generations of Black aviators, including the Tuskegee Airmen during World War II. Pilots flew in her honor. Schools, clubs, and scholarships were named
